有关RFID(射频识别)介绍
什么是RFID(射频识别)?
What is RFID (radio frequency identification)?
RFID(射频识别)是一种无线通信形式,它利用电磁频谱射频部分中的电磁或静电耦合来唯一地识别物体、动物或人。
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.
RFID如何工作?
How does RFID work?
每个 RFID 系统都由三个组件组成:扫描 天线、 收发器和应答器。当扫描天线和收发器组合在一起时,它们被称为 RFID 读取器或询问器。 RFID 阅读器有两种类型:固定阅读器和移动阅读器。 RFID 阅读器是一种联网设备,可以是便携式的,也可以是永久连接的。它使用无线电波传输激活标签的信号。一旦激活,标签就会将波发送回天线,并在天线处转换成数据。
应答器位于 RFID 标签本身中。 RFID 标签的读取范围因标签类型、阅读器类型、RFID 频率以及周围环境或其他 RFID 标签和阅读器的干扰等因素而异。具有更强电源的标签也具有更长的读取范围。
Every RFID system consists of three components: a scanning antenna, a transceiver and a transponder. When the scanning antenna and transceiver are combined, they are referred to as an RFID reader or interrogator. There are two types of RFID readers -- fixed readers and mobile readers. The RFID reader is a network-connected device that can be portable or permanently attached. It uses radio waves to transmit signals that activate the tag. Once activated, the tag sends a wave back to the antenna, where it is translated into data.
The transponder is in the RFID tag itself. The read range for RFID tags varies based on factors including the type of tag, type of reader, RFID frequency and interference in the surrounding environment or from other RFID tags and readers. Tags that have a stronger power source also have a longer read range.
什么是RFID标签和智能标签?
What are RFID tags and smart labels?
RFID标签由集成电路(IC)、天线和基板组成。 RFID 标签中对识别信息进行编码的部分称为 RFID 嵌体。
RFID 标签主要有两种类型:
• 有源射频识别。有源 RFID 标签有自己的电源,通常是电池。
• 无源射频识别。无源 RFID 标签从读取天线接收能量,读取天线的电磁波会在 RFID 标签的天线中感应出电流。
还有半无源 RFID 标签,这意味着电池驱动电路,而通信则由 RFID 读取器供电。
低功耗嵌入式非易失性存储器在每个 RFID 系统中都发挥着重要作用。 RFID 标签通常保存不到 2,000 KB的数据,包括唯一标识符/序列号。标签可以是只读的或读写的,其中数据可以由读取器添加或覆盖现有数据。
RFID 标签的读取范围因标签类型、读取器类型、RFID 频率以及周围环境或其他 RFID 标签和读取器的干扰等因素而异。由于电源更强,有源 RFID 标签比无源 RFID 标签具有更长的读取范围。
智能标签是简单的 RFID 标签。这些标签将 RFID 标签嵌入到不干胶标签中,并带有条形码。它们还可用于 RFID 和条形码阅读器。智能标签可以使用桌面打印机按需打印,而RFID标签需要设备。
RFID tags are made up of an integrated circuit (IC), an antenna and a substrate. The part of an RFID tag that encodes identifying information is called the RFID inlay.
There are two main types of RFID tags:
• Active RFID. An active RFID tag has its own power source, often a battery.
• Passive RFID. A passive RFID tag receives its power from the reading antenna, whose electromagnetic wave induces a current in the RFID tag's antenna.
There are also semi-passive RFID tags, meaning a battery runs the circuitry while communication is powered by the RFID reader.
Low-power, embedded non-volatile memory plays an important role in every RFID system. RFID tags typically hold less than 2,000 KB of data, including a unique identifier/serial number. Tags can be read-only or read-write, where data can be added by the reader or existing data overwritten.
The read range for RFID tags varies based on factors including type of tag, type of reader, RFID frequency, and interference in the surrounding environment or from other RFID tags and readers. Active RFID tags have a longer read range than passive RFID tags due to the stronger power source.
smart labels are simple RFID tags. These labels have an RFID tag embedded into an adhesive label and feature a barcode. They can also be used by both RFID and barcode readers. Smart labels can be printed on-demand using desktop printers, where RFID tags require more advanced equipment.
RFID系统有哪些类型?
What are the types of RFID systems?
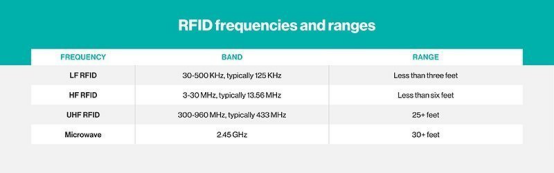
RFID系统主要分为三种类型:低频(LF)、高频(HF)和超高频(UHF)。微波 RFID 也可用。不同国家和地区的频率差异很大。
• 低频 RFID 系统。这些范围从 30 KHz到 500 KHz,但典型频率为 125 KHz。 LF RFID 的传输范围很短,通常从几英寸到不到六英尺。
• 高频 RFID 系统频率范围为 3 MHz至 30 MHz,典型的 HF 频率为 13.56 MHz。标准范围从几英寸到几英尺。
• 超高频 RFID 系统。这些范围从 300 MHz 到 960 MHz,典型频率为 433 MHz,通常可以在 25 英尺外读取。
• 微波 RFID 系统。它们的运行频率为 2.45 Ghz,可以在 30 多英尺外读取。
使用的频率取决于 RFID 应用,实际获得的距离有时与预期不同。例如,当美国国务院宣布将发行配备 RFID 芯片的电子护照时,它表示该芯片只能在大约 4 英寸外读取。然而,国务院很快收到证据表明,RFID 阅读器可以从 RFID 标签中读取信息,距离远超过 4 英寸,有时甚至可达 33 英尺。
如果需要更长的读取范围,使用具有额外功率的标签可以将读取范围扩大到 300 多英尺。
There are three main types of RFID systems: low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF) and ultra-high frequency (UHF). Microwave RFID is also available. Frequencies vary greatly by country and region.
• Low-frequency RFID systems. These range from 30 KHz to 500 KHz, though the typical frequency is 125 KHz. LF RFID has short transmission ranges, generally anywhere from a few inches to less than six feet.
• High-frequency RFID system These range from 3 MHz to 30 MHz, with the typical HF frequency being 13.56 MHz. The standard range is anywhere from a few inches to several feet.
• UHF RFID systems. These range from 300 MHz to 960 MHz, with the typical frequency of 433 MHz and can generally be read from 25-plus feet away.
• Microwave RFID systems. These run at 2.45 Ghz and can be read from 30-plus feet away.
The frequency used will depend on the RFID application, with actual obtained distances sometimes varying from what is expected. For example, when the U.S. State Department announced it would issue electronic passports enabled with an RFID chip, it said the chips would only be able to be read from approximately 4 inches away. However, the State Department soon received evidence that RFID readers could skim the information from the RFID tags from much farther than 4 inches -- sometimes upward of 33 feet away.
If longer read ranges are needed, using tags with additional power can boost read ranges to 300-plus feet.
RFID 应用和使用案例
RFID applications and use cases
RFID 应用和用例
RFID 的历史可以追溯到 20 世纪 40 年代;然而,它在 20 世纪 70 年代使用得更频繁。长期以来,标签和阅读器的高成本阻碍了广泛的商业用途。随着硬件成本的下降,RFID 的采用也有所增加。
RFID 应用的一些常见用途包括:
• 宠物和牲畜追踪
• 库存管理
• 资产跟踪和设备跟踪
• 库存控制
• 货物和供应链物流
• 车辆追踪
• 客户服务和损失控制
• 提高供应链的可见性和分布
• 安全情况下的访问控制
• 船运
• 卫生保健
• 制造业
• 零售销售
• 即按即用信用卡付款
RFID dates back to the 1940s; however, it was used more frequently in the 1970s. For a long time, the high cost of the tags and readers prohibited widespread commercial use. As hardware costs have decreased, RFID adoption has also increased.
Some common uses for RFID applications include:
• pet and livestock tracking
• inventory management
• asset tracking and equipment tracking
• inventory control
• cargo and supply chain logistics
• vehicle tracking
• customer service and loss control
• improved visibility and distribution in the supply chain
• access control in security situations
• shipping
• healthcare
• manufacturing
• retail sales
• tap-and-go credit card payments
RFID 与条形码
RFID vs. Barcodes
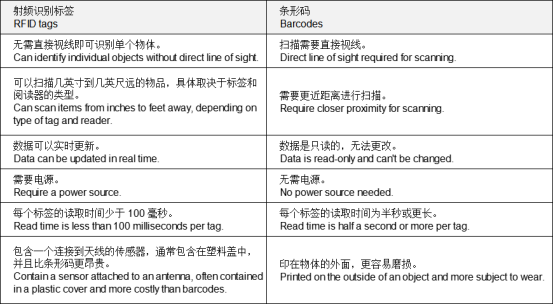
使用 RFID 作为条形码的替代品的使用正在增加。 RFID 和 条形码 技术用于跟踪库存的方式类似,但它们之间存在一些重要的区别。
Using RFID as an alternative for barcodes is increasing in use. RFID and barcode technologies are used in similar ways to track inventory, but there are some important differences between them.
RFID 与 NFC
RFID vs. NFC
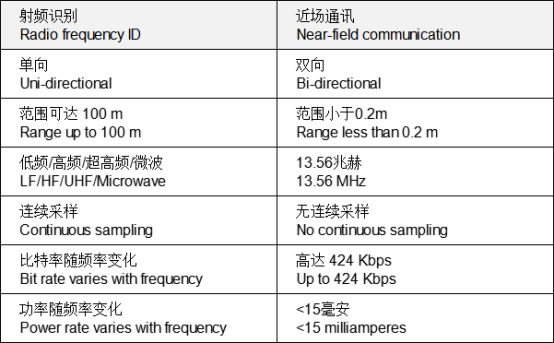
近场通信 (NFC) 通过使用短距离、高频无线通信技术实现设备之间的数据交换。 NFC 将智能卡和读卡器的接口组合到一个设备中。
Near-field communication (NFC) enables data to be exchanged between devices by using short-range, high-frequency wireless communication technology. NFC combines the interface of a smart card and reader into a single device.
RFID挑战
RFID challenges
RFID容易出现两个主要问题:
• 阅读器冲突。当来自一个 RFID 读取器的信号干扰第二个读取器时,可以通过使用防冲突协议使 RFID 标签轮流向其适当的读取器传输信号来防止读取器冲突。
• 标签冲突。当太多标签同时传输数据而使 RFID 读取器感到困惑时,就会发生标签冲突。选择一次收集一个标签信息的阅读器可以防止这一问题。
RFID is prone to two main issues:
• Reader collision. Reader collision, when a signal from one RFID reader interferes with a second reader, can be prevented by using an anti-collision protocol to make RFID tags take turns transmitting to their appropriate reader.
• Tag collision. Tag collision occurs when too many tags confuse an RFID reader by transmitting data at the same time. Choosing a reader that gathers tag info one at a time will prevent this issue.
RFID 安全和隐私
RFID security and privacy
一个常见的 RFID 安全或隐私问题是,任何拥有兼容阅读器的人都可以读取 RFID 标签数据。标签通常可以在物品离开商店或供应链后读取。它们还可以在用户不知情的情况下使用未经授权的阅读器进行读取,并且如果标签具有唯一的序列号,则可以将其与消费者相关联。虽然这是个人隐私问题,但在军事或医疗环境中,这可能是国家安全问题或生死攸关的问题。
由于 RFID 标签没有很强的计算能力,因此它们无法适应加密,例如可能在质询-响应身份验证系统中使用的加密。然而,一个例外是护照中使用的 RFID 标签——基本访问控制 (BAC)。这里,芯片具有足够的计算能力来解码来自阅读器的加密令牌,从而证明阅读器的有效性。
在阅读器处,打印在护照上的信息被机器扫描并用于获取护照的密钥。使用三项信息——护照号码、护照持有人的出生日期和护照的到期日期——以及三项信息中每一项的校验和数字。
研究人员表示,这意味着护照受到密码的保护,其熵比电子商务中通常使用的密码要少得多。它们的密钥在护照的生命周期内也是静态的,因此一旦实体一次性访问了打印的密钥信息,无论是否经过护照持有人的同意,护照都可以读取,直到护照过期。
美国国务院于 2007 年采用了 BAC 系统,在电子护照中添加了防盗材料,以减轻未经发现的窃取用户个人信息的威胁。
A common RFID security or privacy concern is that RFID tag data can be read by anyone with a compatible reader. Tags can often be read after an item leaves a store or supply chain. They can also be read without a user's knowledge using unauthorized readers, and if a tag has a unique serial number, it can be associated to a consumer. While a privacy concern for individuals, in military or medical settings this can be a national security concern or life-or-death matter.
Because RFID tags do not have a lot of compute power, they are unable to accommodate encryption, such as might be used in a challenge-response authentication system. One exception to this, however, is specific to RFID tags used in passports -- basic access control (BAC). Here, the chip has sufficient compute power to decode an encrypted token from the reader, thus proving the validity of the reader.
At the reader, information printed on the passport is machine-scanned and used to derive a key for the passport. There are three pieces of information used -- the passport number, the passport holder's birth date and the passport's expiration date -- along with a checksum digit for each of the three.
Researchers say this means passports are protected by a password with considerably less entropy than is normally used in e-commerce. They key is also static for the life of the passport, so once an entity has had one-time access to the printed key information, the passport is readable with or without the consent of the passport bearer until the passport expires.
The U.S. State Department, which adopted the BAC system in 2007, has added an anti-skimming material to electronic passports to mitigate the threat of undetected attempts to steal users' personal information.
射频识别标准
RFID standards
RFID 技术有多个指南和规范,但主要的标准组织是:
• 国际标准化组织 (ISO)
• 电子产品代码全球公司 (EPCglobal)
• 国际电工委员会 (IEC)
每个射频都有相关标准,包括适用于 LF RFID 的 ISO 14223 和 ISO/IEC 18000-2、适用于 HF RFID 的 ISO 15693 和 ISO/IEC 14443 以及适用于 UHF RFID 的 ISO 18000-6C。
There are several guidelines and specifications for RFID technology, but the main standards organizations are:
• International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
• Electronics Product Code Global Incorporated (EPCglobal)
• International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
Each radio frequency has associated standards, including ISO 14223 and ISO/IEC 18000-2 for LF RFID, ISO 15693 and ISO/IEC 14443 for HF RFID, and ISO 18000-6C for UHF RFID.
By
Sarah Amsler, Senior Managing Editor
Sharon Shea, E xecutive Editor
声明:
- 文章转载自TechTarget,由爱泽工业翻译,如有侵权,请联系删除!
- 如有偏颇,欢迎指正!
上一篇:流量仪表的检验和校准
下一篇:流体污染控制:需要了解的内容

 沪公网安备31011002006738号
沪公网安备31011002006738号

