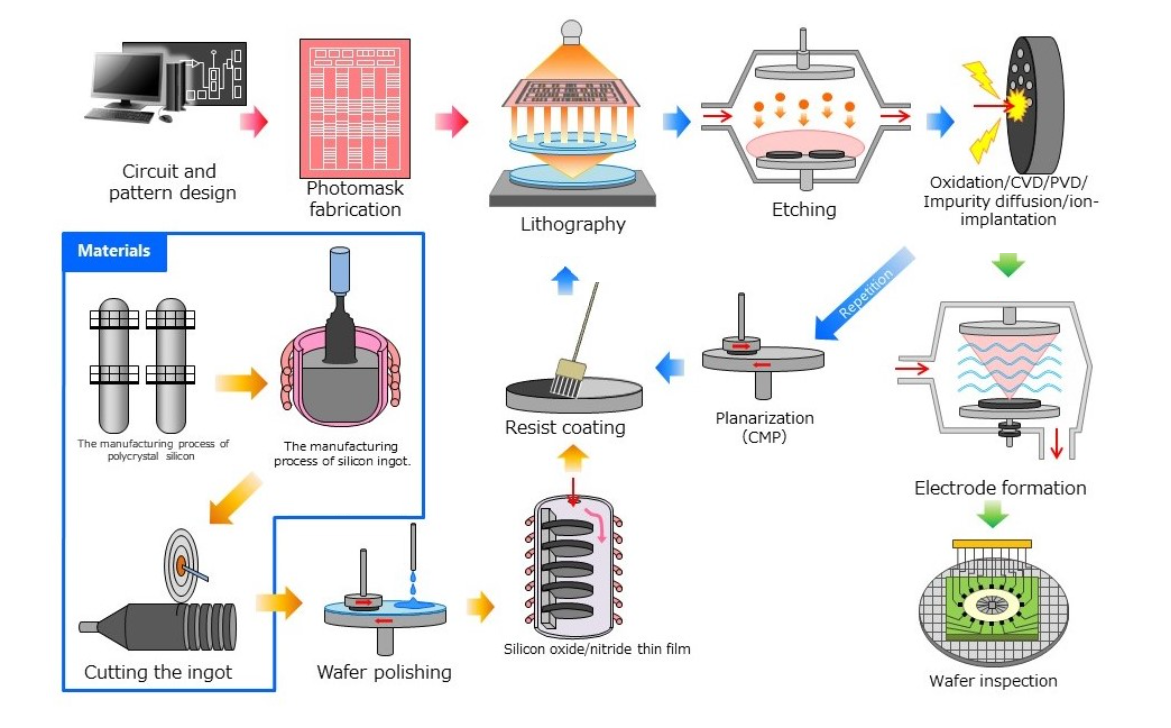
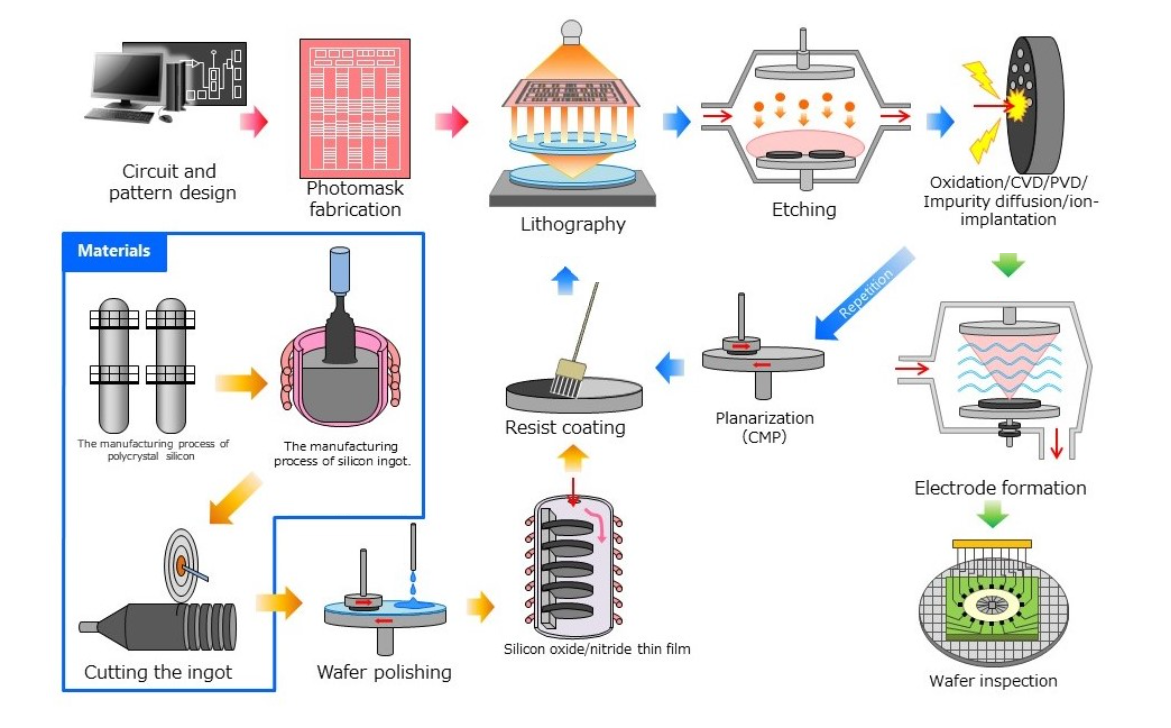
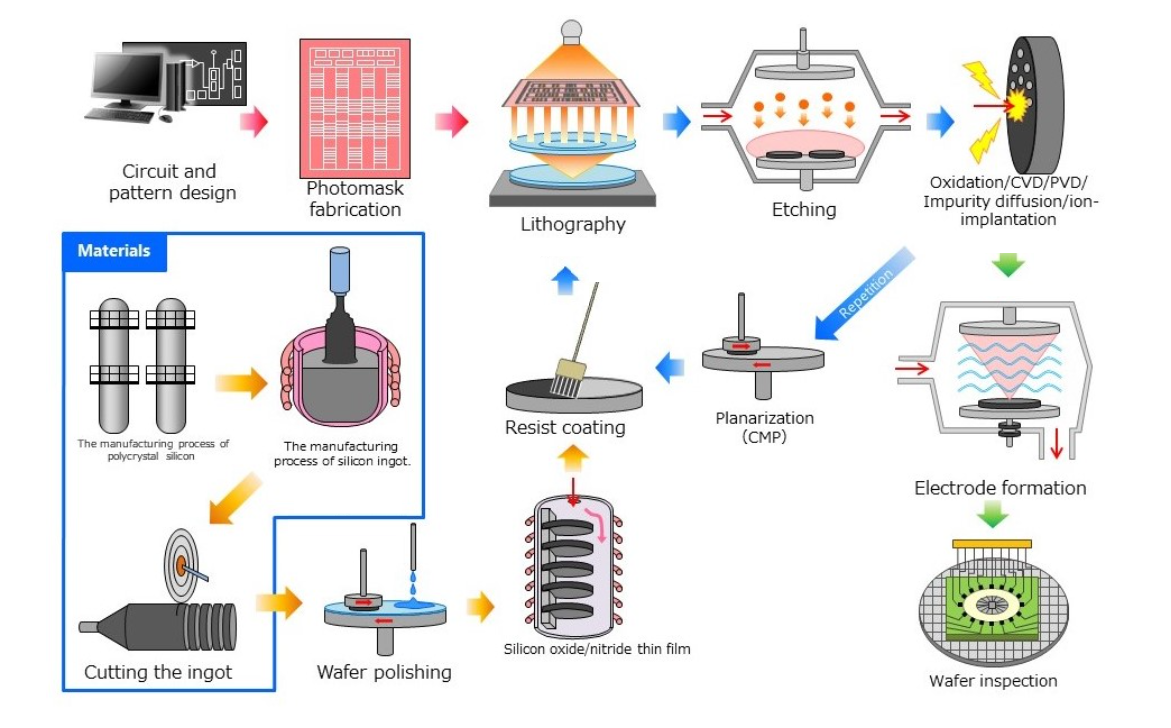
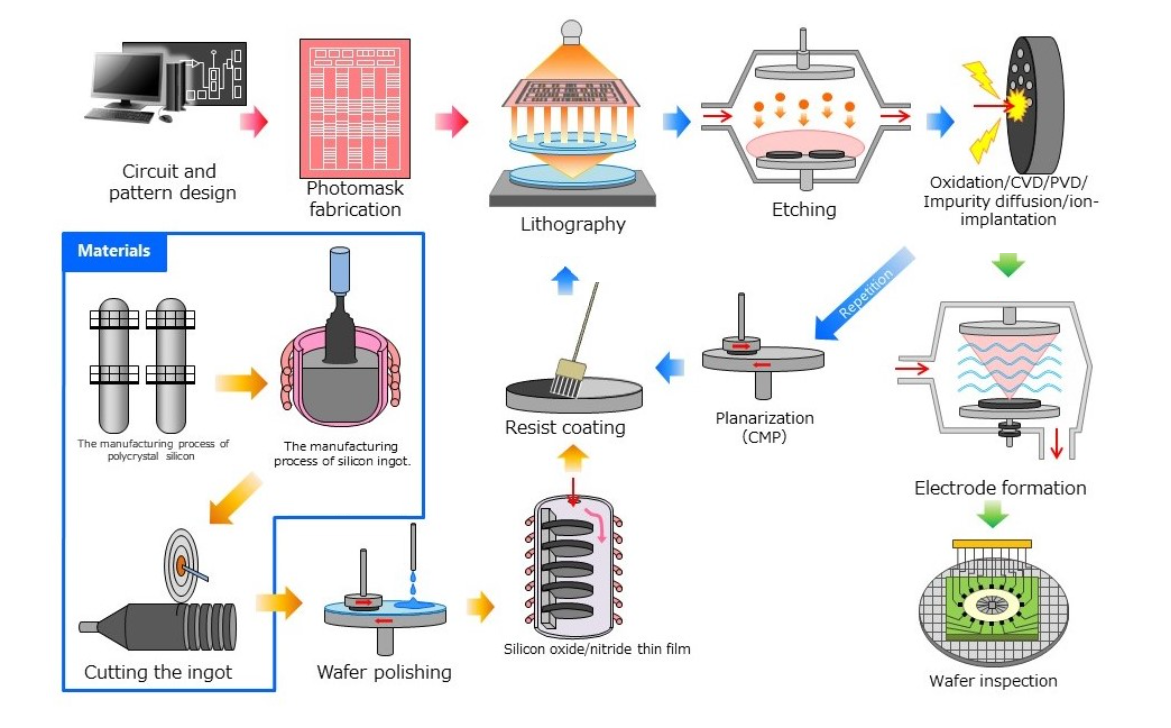
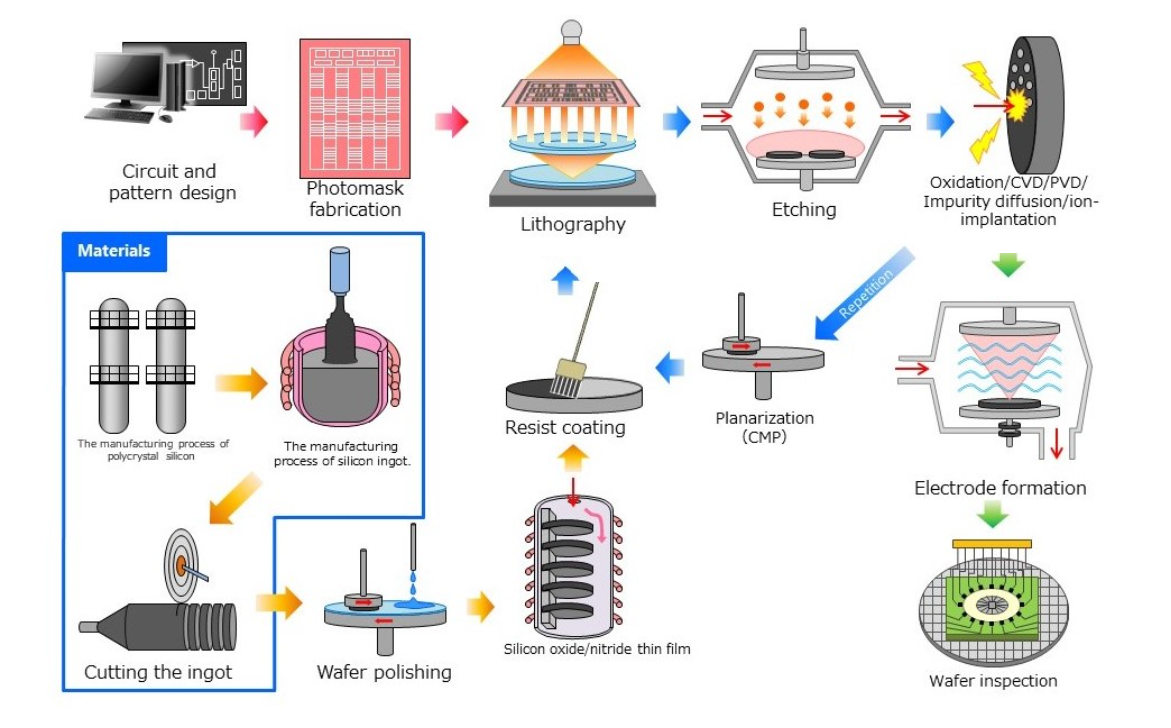
半导体制造前端工艺及气体检测仪的应用
半导体制造(前端工艺)现场
半导体制造过程中使用了多种气体。介绍主要用于各工序气体检测的气体检测仪,并附有相应制造工序的图解。
Semiconductor manufacturing(Front-end process)sites
A wide range of gases are used in semiconductor manufacturing processes. Describes the gas detectors mainly used for detection of gases in each process, accompanied by illustrations of the corresponding manufacturing processes.
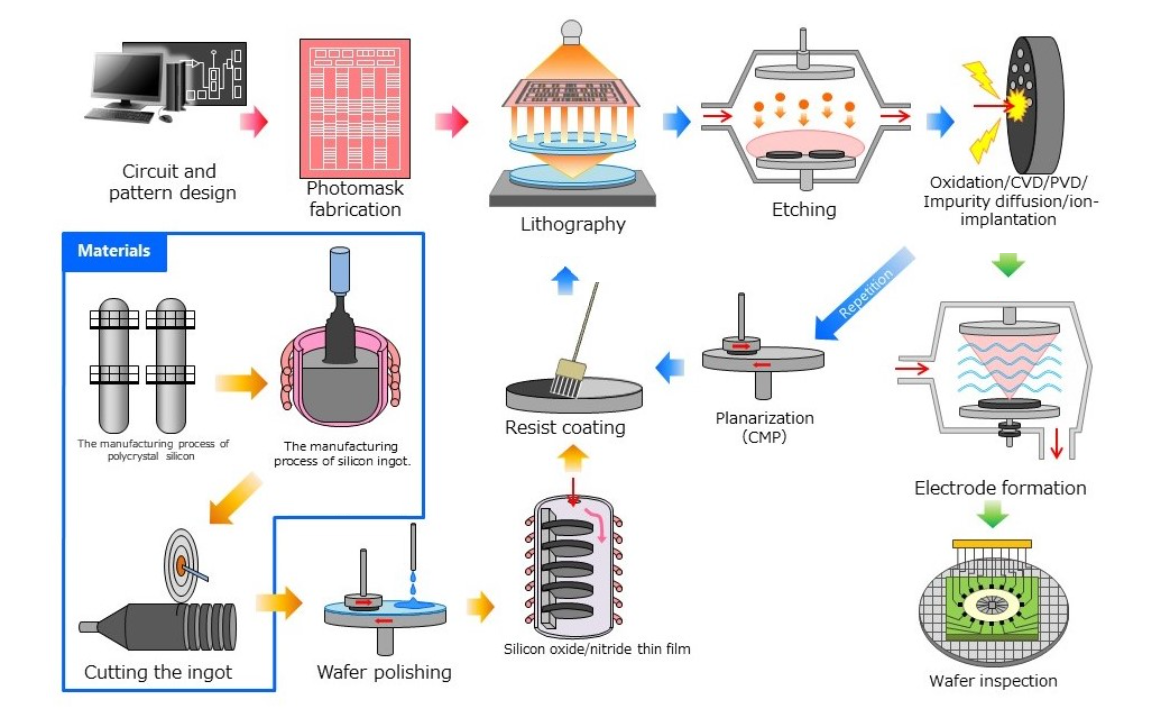
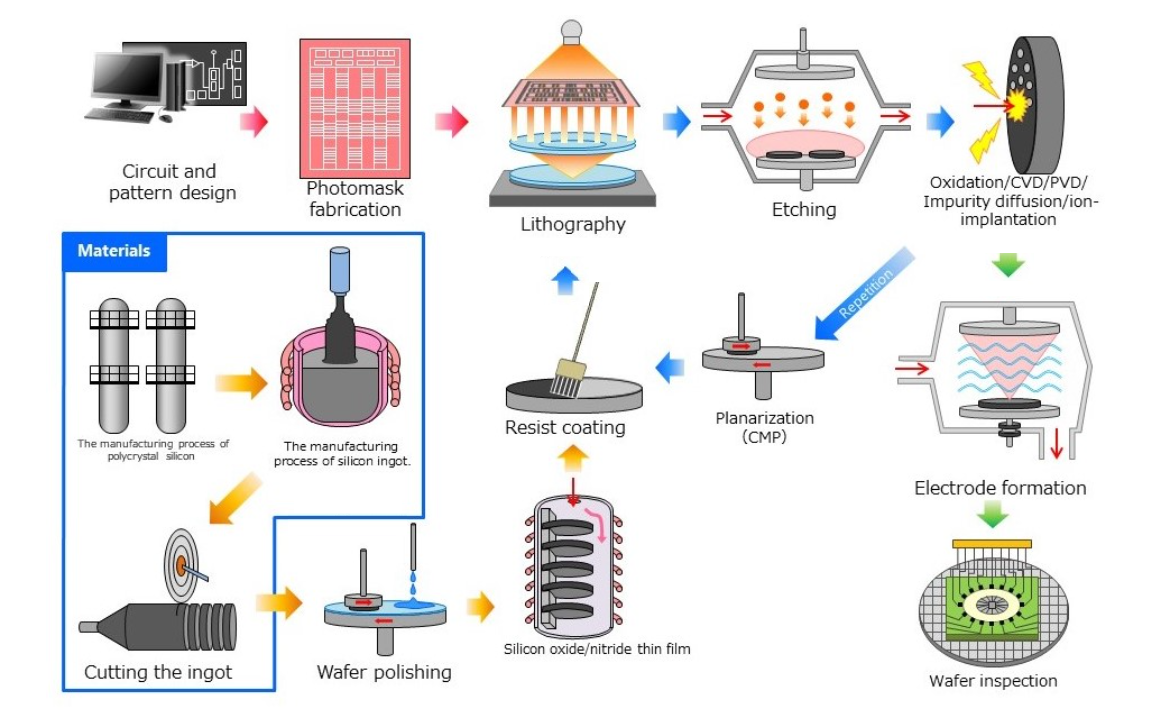
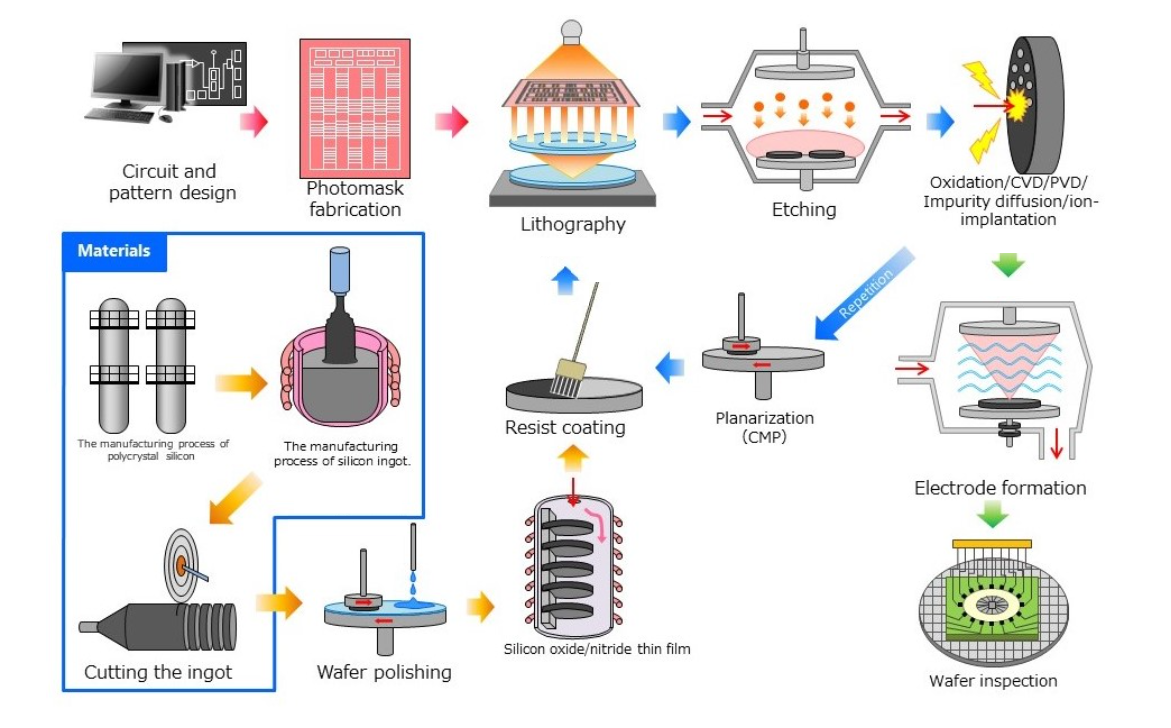
半导体制造工厂前端工序①
Semiconductor manufacturing plant Front-end process ①
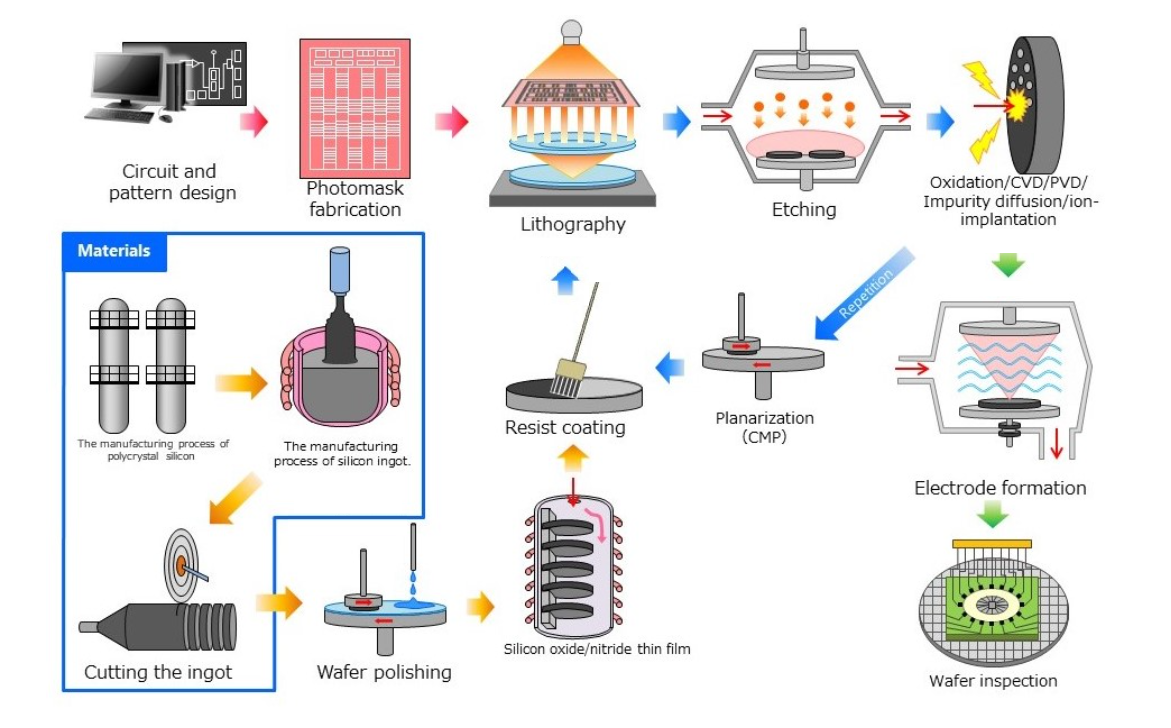
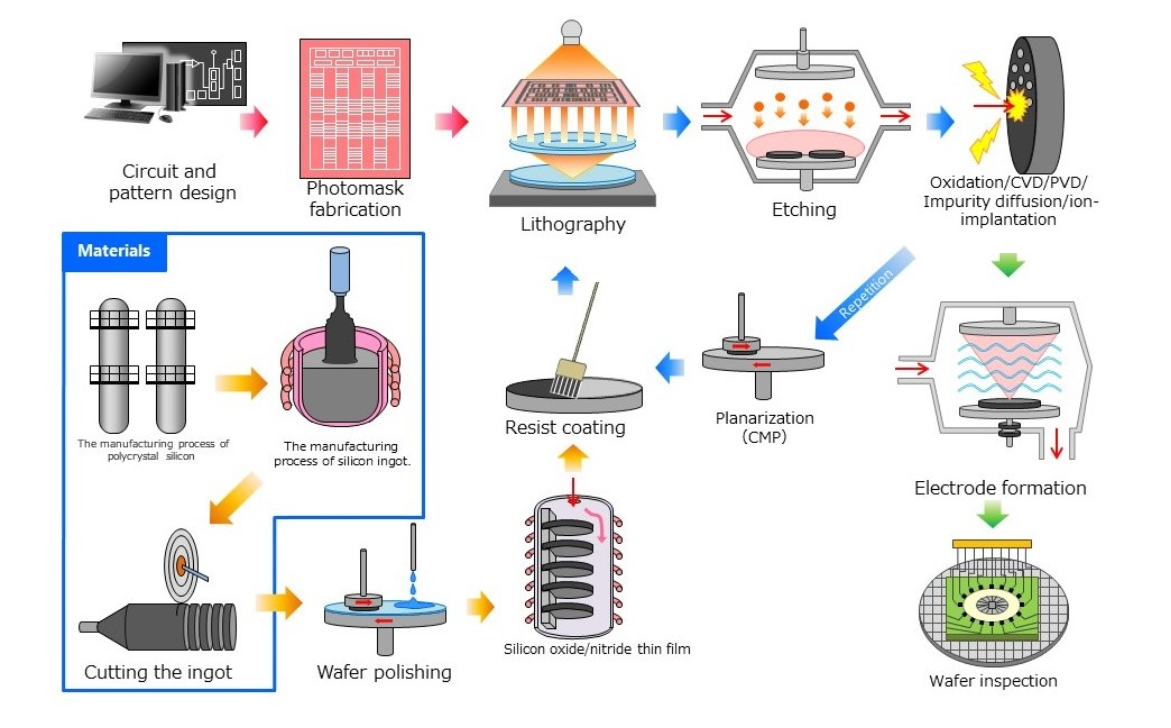
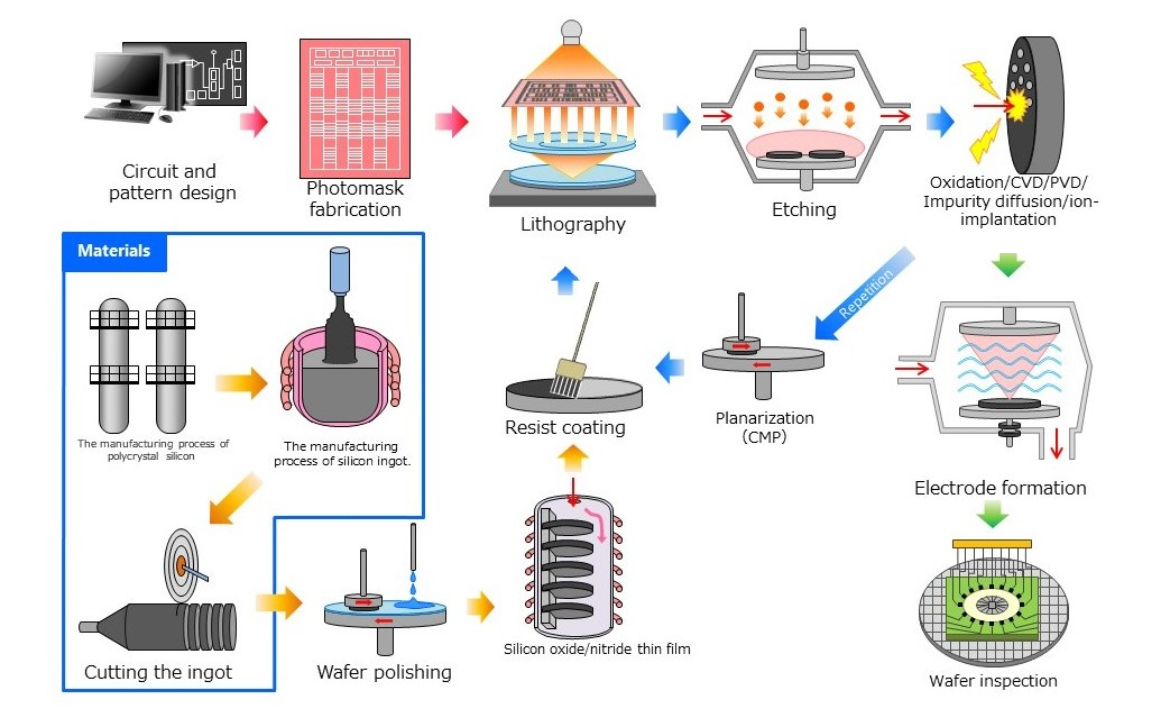
半导体制造工厂前端工序②
Semiconductor manufacturing plant Front-end process ②
多晶硅制造
生产多晶硅包括将金属硅溶解在盐酸 (HCI) 中并精制三氯硅烷 (SiHCI3 ) 以提高纯度。
然后使SiHCI3在反应容器(钟罩)中与超纯氢(H2 )反应以沉淀和生长圆柱形多晶硅。
Polycrystalline Si manufacture
Producing polycrystalline silicon involves dissolving metallic silicon in hydrochloric acid (HCI) and refining trichlorosilane (SiHCI3)to increase the purity.
The SiHCI3 is then allowed to react with ultra-pure hydrogen (H2) in a reaction vessel (bell jar) to precipitate and grow cylindrical polycrystalline silicon.
危害
需要采取预防措施以防止气体泄漏。原料气体和副产物气体含有氢气(H2 )形式的可燃气体和有毒气体如三氯氢硅(SiHCI3 )和氯化氢(HCI)。
Hazards
Precautions are required to prevent gas leaks. The raw material gas and byproduct gas contains combustible gas in the form of hydrogen (H2) and toxic gases such as trichlorosilane (SiHCI3) and hydrogen chloride (HCI).
单晶硅锭制造
单晶硅锭的制造工艺大致分为直拉(CZ)工艺和浮区(FZ)工艺。
这两种工艺都涉及通过在氩气中生长单晶来制造单晶硅锭。
Monocrystalline Si ingot manufacture
Monocrystalline Si ingot manufacturing processes are broadly divided into the Czochralski (CZ) process and the Floating Zone (FZ) process.
Both processes involve manufacturing monocrystalline silicon ingots by growing monocrystals in argon gas.
危害
需要注意工作环境中的氧气浓度,因为制造过程中使用的氩气 (Ar) 是一种会令人窒息的气体。
Hazards
Precautions are required for oxygen concentrations in the work environment, as argon (Ar) used in the manufacturing process is a suffocating gas.
氧化硅膜
氧化硅膜的形成工艺包括热氧化工艺、干式O 2氧化工艺、湿式O 2氧化工艺、热解氧化工艺(包括在外部燃烧氢气和氧气并以水蒸气的形式供应)和盐酸酸氧化过程(包括将氯化氢 (HCl) 气体添加到 N2和 O2气体中)。
Silicon oxide film
Silicon oxide film formation processes include the thermal oxidation process, dry O2 oxidation process, wet O2 oxidation process, the pyrogenic oxidation process (which involves combusting H2 gas and O2 gas externally and supplying this as water vapor),
and the hydrochloric acid oxidation process (which involves adding hydrogen chloride (HCl) gas to N2 and O2 gas).
危害
如果使用氢气 (H2 ) 或氯化氢 (HCI),则需要采取预防措施以防止气体泄漏。
Hazards
Precautions are required to prevent gas leaks if hydrogen (H2) or hydrogen chloride (HCI) are used.
氮化硅薄膜
通过在高温下使硅烷(SiH4 )和氨气(NH3 )发生化学反应,在氧化硅膜的顶部沉积氮化硅膜。
Silicon nitride film
A silicon nitride film is deposited on top of the silicon oxide film by chemically reacting silane (SiH4) and ammonia (NH3) gas at high temperature.
危害
由于硅烷 (SiH4 ) 和氨 (NH3 ) 都是有毒气体,因此需要采取预防措施来防止即使是很小的泄漏。
Hazards
Precautions are required to prevent even small leaks, as both silane (SiH4) and ammonia (NH3) are toxic gases.
光刻
光刻包括用光刻胶涂覆硅晶片的表面,并使用曝光机通过光掩模进行曝光,以从光掩模上转移电路图案。
使用去除剂从暴露的晶片上去除残留的抗蚀剂区域。
Lithography
Lithography involves coating the surface of a silicon wafer with photoresist and exposure via a photomask using an exposure machine to transfer the circuit pattern from the photomask.
The residual areas of resist are removed from the exposed wafer using a remover.
危害
由于 KrF 和 ArF 中使用的氟 (F2) 气体是有毒气体,因此需要采取预防措施以防止即使是很小的泄漏。
Hazards
Precautions are required to prevent even small leaks, as the fluorine (F2) gas used in KrF and ArF is a toxic gas.
化学气相沉积(CVD)
CVD(化学气相沉积)技术涉及通过使原料气体(薄膜生成气体)在反应室中发生化学反应,在晶片上沉积新薄膜。
CVD
The CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) technique involves depositing a new film on a wafer by allowing the raw material gas (film generating gas) to chemically react in a reaction chamber.
危害
由于硅烷 (SiH4 ) 和 TEOS等原料气体是有毒气体,因此即使是很小的泄漏也需要采取预防措施。
Hazards
Precautions are required to prevent even small leaks, as raw material gases such as silane (SiH4) and TEOS are toxic gases.
PVD
PVD(物理气相沉积)技术通过促进等离子体中产生的氩 (Ar) 离子与真空室内的目标碰撞并将喷射的目标原子沉积在晶片上来形成薄膜。
PVD
The PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) technique forms a film by promoting the collision of argon (Ar) ions generated in a plasma against a target inside a vacuum chamber and depositing the ejected target atoms on a wafer.
危害
需要注意工作环境中的氧气浓度,因为制造过程中使用的氩气 (Ar) 是一种令人窒息的气体。
Hazards
Caution is required with the oxygen concentration in the work environment, as the argon (Ar) used in the manufacturing process is a suffocating gas.
外延
外延技术在单晶衬底上形成新晶体。
根据所制造的基材,使用的气体范围很广。
Epitaxial
The epitaxial technique forms new crystals on a monocrystal substrate.
A wide range of gases are used, depending on the substrate being manufactured.
危害
需要采取预防措施以防止诸如硅烷(SiH4)和氢气(H2)等气体的泄漏。
Hazards
Precautions are required to prevent leaks of gases such as silane (SiH4) and hydrogen (H2).
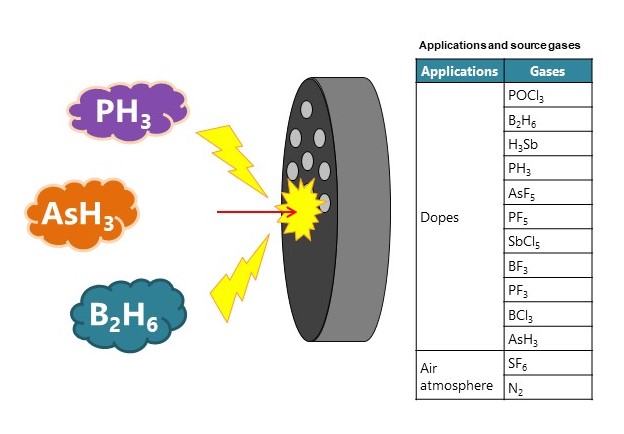
杂质扩散
这是一种有意将微量杂质添加到晶片中以确保有效的半导体功能的技术。
这也称为掺杂,掺杂时使用的气体称为掺杂气体。
Impurity diffusion
This is a technique for intentionally adding trace amounts of impurities to a wafer to ensure efficient semiconductor function.
This is also called doping, and the gas used in doping is called the doping gas.
危害
需要采取预防措施以防止三氟化氯 (CIF3 ) 和乙硼烷 (B2 H6 ) 等气体的泄漏。
Hazards
Precautions are required to prevent leaks of gases such as chlorine trifluoride (CIF3) and diborane (B2H6).
离子注入法(注入)
该技术用于通过电离杂质原子并将它们置于足以驱动它们进入硅晶体的加速度来将杂质注入晶片。
Ion injection method (implanting)
This technique is used to inject impurities into a wafer by ionizing atoms of the impurity and subjecting them to acceleration sufficient to drive them into silicon crystals.
危害
需要采取预防措施以防止诸如磷化氢 (PH3 ) 和乙硼烷 (B2 H6 ) 等气体的泄漏。
Hazards
Precautions are required to prevent leaks of gases such as phosphine (PH3) and diborane (B2H6).
蚀刻
蚀刻是一种利用化学品或气体的腐蚀作用在半导体上形成电路的技术。
蚀刻工艺有两种类型:干法和湿法。
Etching
Etching is a technique for forming circuits on semiconductors using the corrosive action of chemicals or gases.
There are two types of etching processes: dry and wet.
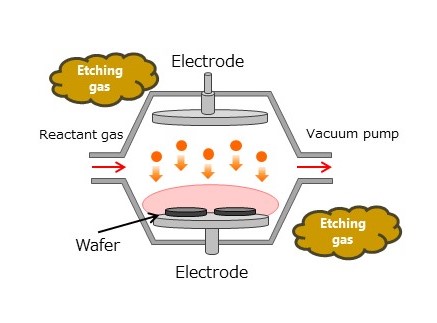
危害
需要采取预防措施以防止气体和溶液泄漏。
干法蚀刻使用的典型气体:CF4、CHF3、CI2、HBr、r、SF6、BCI3等
湿法蚀刻使用的典型溶液:氟化氢(HF)、氟化氢+氟化铵(NH4 F )、热磷酸(H3 PO4 )、氟化氢+硝酸(HNO3 )+含碘冰醋酸(CH3 COOH + I2 )等。
Hazards
Precautions are required to prevent leaks of gases and solutions.
Typical gases used in dry etching: CF4, CHF3, CI2, HBr,r, SF6, BCI3, etc.
Typical solutions used in wet etching: hydrogen fluoride (HF), hydrogen fluoride + ammonium fluoride (NH4F), hot phosphoric acid (H3PO4), hydrogen fluoride + nitric acid (HNO3) + glacial acetic acid containing iodine (CH3COOH + I2), etc.
CMP,洗涤,灰化
CMP(化学机械抛光)是一种抛光技术,用于平滑晶片表面的光洁度。
CMP后需要洗涤,根据洗涤要求使用各种溶液和方法。
CMP,washing,ashing
CMP (Chemical Mechanical Polishing) is a polishing technique for smoothing the finish of a wafer surface.
Washing is necessary following CMP, and various solutions and methods are used depending on the washing requirements.
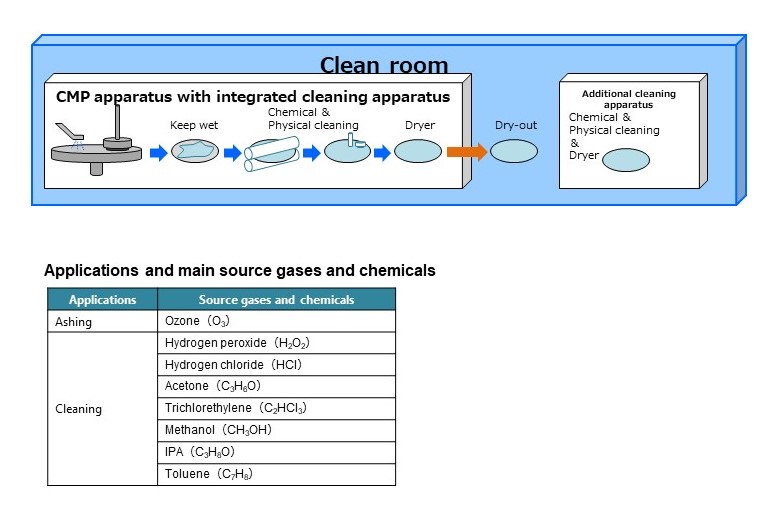
危害
需要采取预防措施以防止过程中使用的气体和溶液泄漏。
Hazards
Precautions are required to prevent leaks of gases and solutions used in the process.
气体检测仪的应用
Gas detectors are used in applications
建议将固定式气体检测仪用于以下应用:
・用于检查工人在场的工作环境的安全性
・用于检测制造工厂和设备的泄漏
Fixed gas detectors are recommended for the following applications:
・ For checking the safety of work environments in which workers are present
・ For detecting leaks from manufacturing plants and equipment
建议将便携式气体检测仪用于以下应用:
・为了加强对工人的安全措施
・ 从维护检查作业前的残留气体确认到作业时的安全性确认、管接头的密封状况确认等客观数据进行安全管理
・ 用于确定发生气体泄漏的位置
Portable gas detectors are recommended for the following applications:
・ For strengthening safety measures for workers
・ For managing safety using objective figures from checking for residual gas before maintenance and inspection work to confirming safety during work and checking sealing conditions on pipe unions
・ For identifying the locations of gas leaks if they occur
本文英文原文转载自:RIKEN KEIKI CO., LTD. https://product.rikenkeiki.co.jp/
本文翻译by爱泽工业,如有偏颇,敬请指正。

 沪公网安备31011002006738号
沪公网安备31011002006738号

